Industrie Nieuws
Understand The Morphology of Laser Spots And Their Application Value
As a high-intensity, highly coherent light source, lasers play a vital role in various fields, including industry and science. A laser spot is the bright spot formed on an object’s surface when the laser pulse emitted by a lidar system encounters it. This bright area is formed by the laser beam’s transmission through space. Its shape and characteristics are also of great significance in laser technology and its applications.
The shape of the laser spot is not fixed. It is affected by many factors and has diverse changing characteristics.
1.Factors affecting laser spot morphology
In general, the morphology of the laser spot is mainly affected by the following factors:
The influence of laser type. Different types of lasers, such as solid lasers and gas lasers, may produce different spot shapes.
Influence of propagation medium. When a light beam propagates in different media (such as air, water, glass, etc.), the morphology of the light spot may also change.
The influence of focusing conditions. Focusing conditions will also affect the shape of the laser spot. The size and shape of the spot can be adjusted by changing the focal length and position of the focusing lens.
Influence of beam quality. The divergence angle, focusing performance, energy distribution and other characteristics of the beam will also affect the shape and size of the spot.
The influence of the observation plane position. The morphology of the light spot on the observation plane at different distances may also be different.
Factors affecting laser spot morphology
2.Common forms of laser spot and its application
The common forms of laser spots are as follows:
(1)Circular light spot
A circular spot is the most common and idealized form of a laser spot, typically formed when a laser beam is focused by an ideal lens. This type of spot is formed due to the relatively uniform intensity distribution in all directions of the laser beam. Its main application values are as follows:
Material processing: In applications such as cutting and drilling, uniform energy distribution produces more uniform processing results.
Lithography and exposure: A uniform light spot helps achieve consistent exposure results, especially in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing that require high-precision marking.
Optical communications: Good preservation of mode quality during transmission in optical fibers.
(2)Elliptical spot
In some cases, due to the design of the optical system or the non-uniformity of the beam, the light spot may appear elliptical. For example, when the cross section of the laser beam has an intensity gradient in a certain direction, the light spot formed after focusing may appear elliptical. Its main application value is as follows:
Specific processing: The special proportion of the elliptical spot can be used for directional processing, such as pulling up long strips and cutting.
Image scanning: Used for scanners and barcode readers to adapt to different scanning needs.
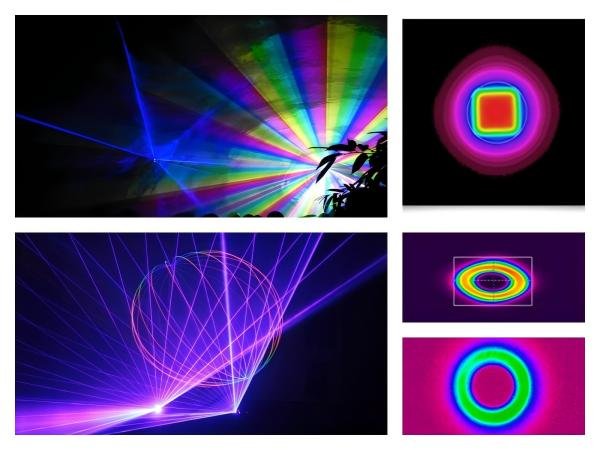
Common forms of laser spots
(3)Multifocal spot
A multifocal spot is a special type of spot that usually appears after a laser beam passes through a complex optical system. These optical systems may contain multiple lenses, mirrors, or diffraction elements, which work together to form multiple focal points at different locations on the laser beam. Its main application value is as follows:
It is used in laser micromachining, laser medicine and other fields, such as for processing multiple tiny target areas at the same time.
(4)Ring-shaped spot
The light spot of annular spot is annular and can be produced by phase plate or multimode interference. Usually the light intensity in the center area is lower and it is often used in special applications. Its main application value is:
Drilling: Suitable for processing that requires drilling hollow holes in material surface coatings or films.
Laser transmission and communication: Used in measurement systems to reduce light loss due to reflection.
(5)Irregular light spot
The irregular spot is the most complex type of laser spot shape, which may be caused by a variety of factors, such as the non-ideal output of the laser, the strong diffraction effect of the light beam, the inhomogeneity of the propagation medium, defects in the optical components, etc., resulting in the asymmetric shape of the spot.
Due to the uneven energy distribution, irregular light spots usually need to be corrected, but in some experimental studies, this property can be used to study special optical effects.
In short, by properly adjusting the shape of the laser spot, the efficiency and effectiveness of laser applications can be improved. Engineers and researchers often use optical simulation software and experimental methods to optimize the shape of the spot to achieve ideal application results.

Common applications of laser spots
3.Laser spot characteristic measurement
Measuring the characteristics of the light spot is crucial for application optimization and process control. There are some common measurement methods:
(1)Knife-edge method: The knife-edge method is a simple method for measuring spot size and divergence angle.
(2)Camera measurement: Use a high-resolution camera to directly capture the light spot image and calculate the size and shape of the light spot.
(3)Power detector scanning: Use a detector to measure the light intensity at different positions to obtain the energy distribution of the light spot.
4.Laser spot detection technology
Laser spot detection is a key step in evaluating the quality and characteristics of laser beams. There are many different detection methods, including:
(1)Beam Profiler: By measuring the intensity distribution of the laser spot and combining it with the M² (Beam Quality Factor) measurement extension kit, the M² value of the beam can be calculated, thus comprehensively evaluating the beam quality.
(2)Thermal imaging method: Use thermal imaging equipment such as infrared thermal imagers to capture the thermal effect generated when the laser beam irradiates the target surface, and detect the spot parameters by analyzing the thermal image.
Laser spot detection technology
(3)CCD or CMOS-based machine vision system: Uses a high-resolution CCD or CMOS camera to capture the image of the laser spot, and then uses image processing software to analyze the size, shape, energy distribution and other characteristics of the spot.
(4)Quadrant detector (QPD) and PSD (position sensitive detector): Determine the position of the center of the light spot by comparing the light intensity of each part.
With the continuous development of science and technology, the research and application of laser spots will continue to deepen and expand. In the future, the application of laser spots will be more extensive, bringing new opportunities and challenges to social development.

